
Cabo Verde EU Cooperation
The West African Corridor
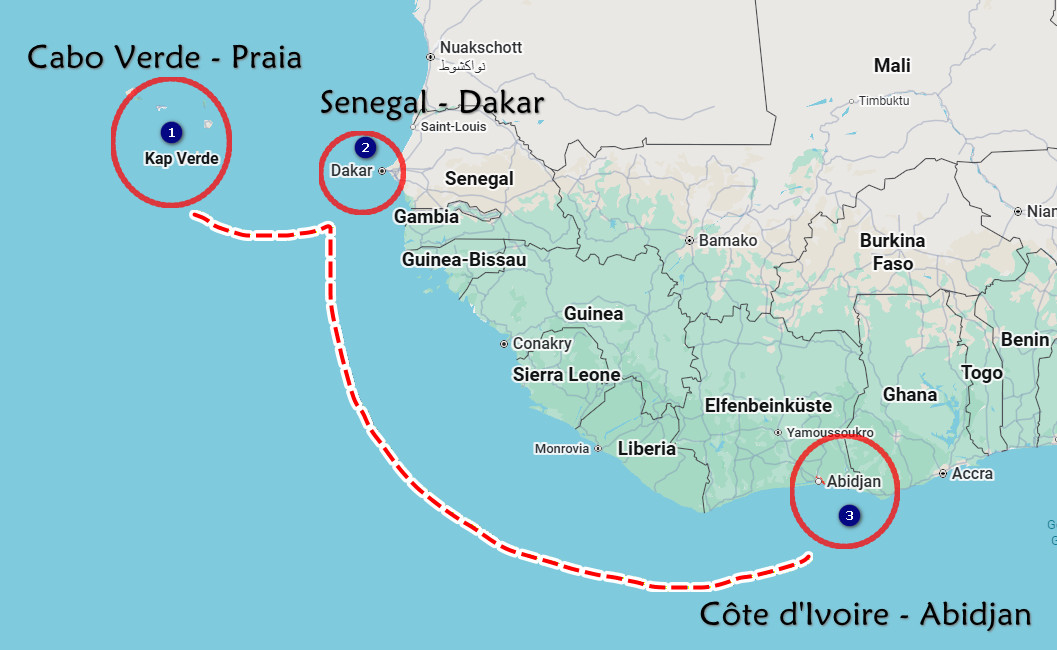
The Praia-Dakar-Abidjan transport corridor
The corridor is supported by "Team Europe" (the EU, its Member States)
The Praia-Dakar-Abidjan multimodal transport corridor is a specific strategic initiative identified under the European Union's Global Gateway Africa-Europe Investment Package.
Here are the key details regarding this corridor:
1. Scope and Geography
- Route: The corridor is designed to connect coastal West African nations, linking the island nation of Cabo Verde (Praia) with the mainland through Senegal (Dakar) and extending down to Côte d'Ivoire (Abidjan).
- Countries Involved: The corridor encompasses Cabo Verde, Senegal, The Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Côte d'Ivoire.
- Objective: The primary goal is to integrate African and European multimodal transport networks to facilitate smart, fair, and affordable mobility and trade within Africa and between the two continents. It aims to support value chains and boost economic integration within the West African region.
2. Specific Projects and Investments
The corridor is supported by "Team Europe" (the EU, its Member States, and financial institutions like the EIB) in collaboration with partners such as the African Development Bank (AfDB). Several specific infrastructure projects constitute this corridor:
-
In Cabo Verde (Maritime Node):
- Port Modernization: The expansion and modernization of strategic ports are directly linked to this corridor to integrate the archipelago into the regional logistics network. This includes the expansion of Porto Grande (Mindelo, São Vicente), Porto Novo (Santo Antão), and Porto da Palmeira (Sal).
- Maio and Sal Investments: A blended financial operation of €38.1 million (including a €17 million EU grant) was designated for the expansion and modernization of the Port of Inglês in Maio and the Port of Palmeira in Sal to increase capacity and physical resilience.
- Strategic Role: These investments are intended to transform Cabo Verde's ports into a regional center of excellence and a logistic hub in the Atlantic, unifying the country's scattered market with the wider region.
-
In Liberia:
- Road Rehabilitation: The corridor initiative includes the rehabilitation of the Mano River Union Road, specifically paving the 47.1 km Sanniquellie to Loguatuo road section.
- Border Infrastructure: It also funds the construction of a one-stop border post at the Loguatuo/Gbeunta/Danane border between Liberia and Côte d'Ivoire to reduce transport costs and facilitate the free movement of goods and people.
- Financing: This specific action involves a €53.8 million blended financial operation with the EIB and the AfDB.
-
In Senegal:
- Transport Upgrades: Senegal is a main beneficiary of the regional project, with investments targeting the upgrade and operation of the port of Ziguinchor and the development of mobility services in the Dakar area, such as the electric Bus Rapid Transit system.
3. Strategic Context
This corridor is one of 11 strategic corridors identified to enhance EU-Africa connectivity. It operates alongside other major West African corridors, such as the Abidjan-Lagos corridor and the Abidjan-Ouagadougou corridor.

.
The 11 strategic transport corridors to enhance connectivity between Africa and Europe
The European Union's Global Gateway initiative has identified 11 strategic transport corridors to enhance connectivity between Africa and Europe, boost trade and mobility, and support sustainable infrastructure across the continent. These corridors are aligned with the African Union's Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa (PIDA) and are intended to strengthen both intra-African and Africa-EU links. International Partnerships
The 11 EU-Africa Strategic Corridors
-
Abidjan–Lagos (West Africa) — Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria International Partnerships
-
Abidjan–Ouagadougou (West Africa) — Côte d'Ivoire, Burkina Faso International Partnerships
-
Praia/Dakar–Abidjan (West Africa) — Cabo Verde, Senegal, Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire International Partnerships
-
Cotonou–Niamey (West Africa) — Benin, Niger International Partnerships
-
Libreville/Kribi/Douala–N'Djamena (Central Africa) — Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Chad, São Tomé and Príncipe International Partnerships
-
Douala/Kribi–Kampala (Central Africa) — Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Uganda International Partnerships
-
Mombasa–Kisangani (East Africa) — Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo International Partnerships
-
Dar es Salaam–Nairobi–Addis Ababa–Berbera–Djibouti (East Africa) — Tanzania, Kenya, Ethiopia, Somalia, Djibouti International Partnerships
-
Maputo–Gaborone–Walvis Bay–Lüderitz (Southern Africa) — Mozambique, South Africa, Eswatini, Botswana, Namibia JRC: EU Science Hub
-
Durban–Lusaka–Lubumbashi (Southern Africa) — South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Zambia, DRC JRC: EU Science Hub
-
Cairo–Khartoum–Juba–Kampala (North & East Africa) — Egypt, Sudan, South Sudan, Uganda (assessment for this corridor is pending) JRC: EU Science Hub
.
